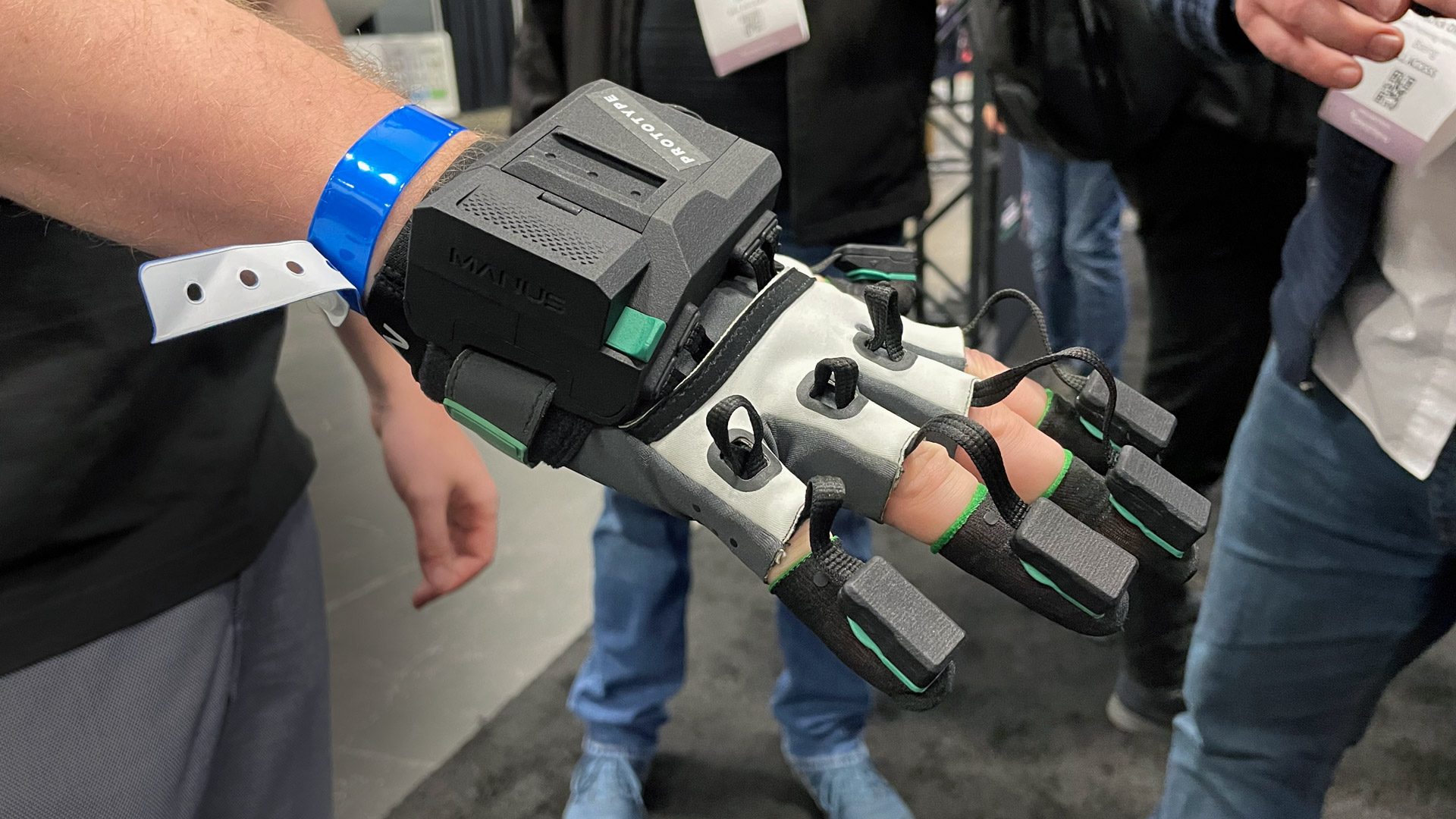
At GDC 2022 this week, VR glove creator Manus revealed its new Quantum Metagloves which the company says delivers significantly more accurate finger tracking than its prior solutions. Though priced for enterprise use, the company says it one day hopes to deliver the tech to consumers.
Manus has been building motion gloves for use in real-time VR and motion capture for years now, with prior offerings being based on IMU and flex-sensor tracking.
The company’s latest product, the Quantum Metagloves, moves to a new magnetic tracking approach which purportedly offers significantly more accurate finger tracking, especially when it comes to self-contact (ie: fingers touching other fingers or the palm of the hand).
Revealed at GDC 2022 for the first time, Manus showed off a demo of the Quantum Metagloves using a realistic real-time hand model that mirrored the wearer’s finger movements. Though the gloves are designed to work in conjunction with 6DOF tracking (via a SteamVR tracker or other motion tracking tech), the GDC demo didn’t employ 6DOF (which is why the visualization of the arm rotates in place). The latency reflected in this setup is also purportedly not representative of the actual tracking latency.
The Quantum Metagloves have a magnetic base positioned on the back of the palm while each finger has a module on the tip that is sensed within the magnetic field. Manus says this means the gloves can detect absolute finger length and width (once calibrated), which enables more accurate hand-tracking when combined with an underlying skeletal model of the hand that is scaled dynamically to the user.

In the video I asked the demonstrator to make a handful of different poses. Indeed, finger-to-finger and finger-to-palm contact looked impressive with no obvious clipping or stuttering. The company told me the demo wasn’t specially programmed to make clipping impossible and that the behavior was purely thanks to the positional data of the sensors which was described as “very clean” compared to alternative approaches to finger tracking.
Manus says the Quantum Metagloves are unique in this way, as other finger tracking technology tends to break down in these sorts of close-contact and self-contact scenarios, especially when both hands are near or touching each other. Even expensive optical tracking systems (with markers on the tips of each finger) can be foiled easily by self-occlusion or one hand occluding the other. Similarly, purely IMU-based finger tracking is prone to drift and requires regular recalibration.
But magnetic tracking is by no means perfect. In other magnetic tracking systems we’ve seen challenges with latency and electromagnetic interference.
Manus admitted that holding metallic or electronic items could throw off the tracking, but says it worked hard to ensure the gloves don’t interfere with each other; up to eight gloves can be active near each other without interference issues, the company says.
While self-contact looked generally quite good with the Quantum Metagloves, other poses didn’t fare quite as well—like a completely clenched first. The demonstrator suggested this would be improved easily with a more robust calibration process that included similar poses; whereas they say the calibration used for the demo at GDC was designed to be quick and easy for purposes of the show.
While the finger tracking did look great in many of the demos I saw, some of the other demo gloves on display showed much less accuracy. This was chalked up to “calibration,” though a big question for such systems is how much said calibration drifts over time and whether the periods between recalibration are practical for a given use-case.
In any case, use-cases will be deeply constrained by price; Manus says a pair of the Quantum Metagloves will cost $9,000, with pre-orders opening in April and shipments expected by the end of Q3. The company says it also plans to launch a haptic version of the Quantum Metagloves which will include per-finger haptics to enhance immersion in VR.
Manus maintains that it would like to bring its gloves to consumers one day, but says the number of custom parts and manufacturing makes it difficult to get the price down to a reasonable level.